Cyber Law, Cyber Security, Privacy, Data Protection Blog - FREE TO SHARE
Tuesday, June 21, 2016
Sunday, June 5, 2016
Terrorist using Customised Apps to evade detection
Terrorist have created an application 'calculator' which can be downloaded on smart phones attached to the off-air network created specifically for them.
The technology is based on the concept of 'cognitive digital radio' that enables users to turn their smartphones into peer-to-peer, off-grid communication tools.
The network generates its own signal through proprietary adhoc networking protocols and automatically coordinates with other units within range which enables users to send and receive text messages, share their GPS locations on offline maps regardless of access to WiFi or cellular service.
The technology is based on the concept of 'cognitive digital radio' that enables users to turn their smartphones into peer-to-peer, off-grid communication tools.
The network generates its own signal through proprietary adhoc networking protocols and automatically coordinates with other units within range which enables users to send and receive text messages, share their GPS locations on offline maps regardless of access to WiFi or cellular service.
The Calculator app is loaded on a normal Android phone and communicates over WiFi to the Radio which further gets transmitted on VHF as digital burst communication.
The principle is same as Gotennna but with little difference.
Gotennna uses Bluetooth to communicate with the a small Radio device Antenna which further uses UHF to transmit data.
Gotennna works on P2P concept while this most likely is not working on P2P.
Terrorist are also using morse code and DTMF to evade interception.
#cyberenabledterrorism #cyberterrorism
Wednesday, May 25, 2016
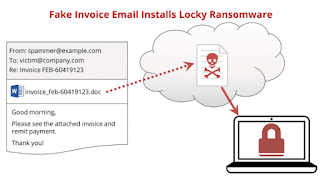
What is Locky Malware and what to do
is a Malware(virus types) which is sent to your computer via email or via an attachment of a fake invoice then that malware(malicious software) encrypts your hard disk and whole data becomes meaningless like special characters ं$#़॥ like this only one jpg file u can open.
Then only in this jpg file there are instructions to pay ransome via bitcoin. Once u pay the hard disk is decrypted I.e made meaningful.
The victim receives an email that requests payment on an attached "invoice", usually a Word file. The attachment contains some sort of executable code, like a VBA macro, that downloads the actual malware from a web site and runs it, encrypting the data on the victim's local and networked hard drives. It then displays a screen that demands a ransom to decrypt the data.
The victim receives an email that requests payment on an attached "invoice", usually a Word file. The attachment contains some sort of executable code, like a VBA macro, that downloads the actual malware from a web site and runs it, encrypting the data on the victim's local and networked hard drives. It then displays a screen that demands a ransom to decrypt the data.
WHAT TO DO WITH LOCKY?
Backup regularly and keep a recent backup copy off-site. There are dozens of ways other than ransomware that files can suddenly vanish, such as fire, flood, theft, a dropped laptop or even an accidental delete. Encrypt your backup and you won’t have to worry about the backup device falling into the wrong hands. Don’t enable macros in document attachments received via email. Microsoft deliberately turned off auto-execution of macros by default many years ago as a security measure. A lot of malware infections rely on persuading you to turn macros back on, so don’t do it!Be cautious about unsolicited attachments. The crooks are relying on the dilemma that you shouldn’t open a document until you are sure it’s one you want, but you can’t tell if it’s one you want until you open it. If in doubt, leave it out. Don’t give yourself more login power than you need. Most importantly, don’t stay logged in as an administrator any longer than is strictly necessary, and avoid browsing, opening documents or other “regular work” activities while you have administrator rights.Consider installing the Microsoft Office viewers. These viewer applications let you see what documents look like without opening them in Word or Excel itself. In particular, the viewer software doesn’t support macros at all, so you can’t enable macros by mistake!Patch early, patch often. Malware that doesn’t come in via document macros often relies on security bugs in popular applications, including Office, your browser, Flash and more. The sooner you patch, the fewer open holes remain for the crooks to exploit.
..Advocate Prashant Mali
Cyber Security & Law Expert
Thursday, April 28, 2016
Meeting with Dr. Jamie Saunders
Wednesday, April 27, 2016
Fast Flux Networks An Introduction
A Fast Flux Network is a network of compromised computers and some public DNS records that change frequently. As a result, the IP address associated with the corresponding domain name changes frequently. This technique is often used by the attackers to hide their malicious websites from detection. Botnets are large groups of compromised machines (bots) used by miscreants for the most illegal activities (e.g., sending spam emails, denial-of-service attacks, phishing and other web scams). To protect the identity and to maximise the availability of the core components of their business, miscreants have recently started to use fast-flux service networks, large groups of bots acting as front-end proxies to these components. Motivated by the conviction that prompt detection and monitoring of these networks is an essential step to contrast the problem posed by botnets,
Attackers typically compromise one or more victim computer systems with malware and exploit those to establish a fraudulent website like a Phishing website. The problem of the attackers with this approach is, these websites can be easily tracked down by public DNS name and IP address to shut them down immediately.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) botnets have emerged as a serious threat against the network security. They are used to carry out various illicit activities like click fraud, DDOS attacks and for information exfiltration. These botnets use distributed concept for command dissemination. These botnets are resilient to dynamic churn and to take-down attempts. Earlier P2P botnet detection techniques have some shortcomings such as they have less accuracy, unable to detect stealthy botnets and advanced botnets using fast-flux networks. In this paper, we list recent P2P botnet detection techniques that overcome the weaknesses of previous techniques with higher detection accuracy.
So, the attackers started using server address obfuscation. They often use a group of proxy servers to redirect network. But, this approach also does not prove to be much convenient for them because of limited scalability. Moreover, these websites can still be tracked down quickly by international cooperation.
So, the attackers started using Fast Flux Networks.
The basic idea behind a Fast Flux Network is to associate multiple IP addresses to a malicious domain name. These IP addresses are swapped in and out with extremely high frequency, may be in every 3 minutes, with the help of changing DNS records. As a result, a browser connecting to the same malicious website in every three minutes will see different IP address each time and connect to the actual malicious website via different infected computers every time.
In Fast Flux Networks, attackers compromise a number of computer systems with malware and then exploit their bandwidth and computation power to build the Fast Flux Network.
In Fast Flux Networks, attackers often use a number of compromised computers as front end systems. These front end systems get the requests from the victims to connect to the malicious website and redirect those requests to the back-end servers.
So, the large pool of rotating IP addresses do not correspond to the actual back-end servers. Instead, they fluctuate among many front end servers which in turn funnel the requests and redirect them to the actual back-end servers.
Fast Flux motherships are the main controlling elements behind the front end servers. They are similar to Command & Control or C & C servers, though they have much more features compared to the C & C servers.This mothership node is hidden by the front end servers, which make them extremely difficult to track down. They often host both DNS and HTTP services and use web server virtual hosting configuration to manage content availability.
Fast Flux Networks are responsible for many illegal practices like online pharmacy shops, money mule recruitment sites, phishing websites, illegal adult contents, distribution of malware etc. Even other services like SMTP, POP, IMAP etc can be delivered using Fast Flux Networks.
image courtesy : Wikipedia
Sunday, April 24, 2016
Monday, April 4, 2016
Black Software List
This List is Public 😇
🔵 Password Hacking Software
1.haviz
2.metasploit
3.hydra
4.wireshark
5.Dsniff
6.InSSIDer
7.Aircrack-ng
8.Aircrack
9.Brutus
10.Cain And Abel
11.IKECrack
🔴Wireless Hacking Software
12.Kismet
13.KisMAC
14.Firesheep
15.NetStumbler
16.WepLab
🔵Network Hacking Software
17.Map
18.SuperScan
19.Angry IP Scanner
🔴Packet Crafting To Exploit Firewall Weaknesses software
20.Hping
21.Scapy
22.Netcat
23.Yersinia
24.Nemesis
25.Socat
🔵Traffic Monitoring for Network Related Hacking software
26.Splunk
27.Nagios
28.P0f
29.Ngrep
🔵Packet Sniffers To Analyze Traffic software
30.Wireshark
31.Tcpdump
32.Ettercap
33.Dsniff
34.EtherApe
35.Paros
36.Fiddler
37.Ratproxy
38.Sslstrip
39.SSL/TLS Security
🔴Test By High-Tech Bridge
Rootkit Detectors To Hack File Systemsoftware
40.Netfilter
41.PF: OpenBSD Packet Filter
42.Skipfish
43.Wfuzz
44.Wapiti
45.W3af
46.Sleuth Kit
47.Helix
48.Maltego
49.Encase
🔴Debuggers To Hack Running Programs software
50.Immunity Debugger
51.Netcat
52.Traceroute
53.Ping.eu
54.Dig
55.CURL
🔵Hacking Operating Systems software
56.Backtrack 5r3
57.Kali Linux
58.SELinux
59.Knoppix
60.BackBox Linux
61.Pentoo
62.Matriux Krypton
63.NodeZero
64.Blackbuntu
65.Samurai Web Testing Framework
66.WEAKERTH4N
67.OpenSSL
68.Open PuTTy
69.Tor
70.openvpn
72.Stunnel
73.KeePass
🔴Intrusion Detection System And The IDS Tools
74.Snort
75.NetCop
🔵Hacking Vulnerability Exploitation Tools
76.Sqlmap
77.Sqlninja
78.Social Engineer Toolkit
79.NetSparker
80.BeEF
81.Dradis
🔵Vulnerability Scanners tools
82.nessus
83.OpenVAS
84.Nipper
85.Secunia PSI
86.Retina
87.QualysGuard
88.NexPose
🔴Web Vulnerability Scanners tools
89.Burp Suite
90.Webscarab
91.Websecurify
92.Nikto
93.W3af
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
FIR : All you want to know about in a criminal case
FIR - What is? The first information report is a report giving information of the commission of a cognizable crime, which may be made by t...

-
Cross-Examination in cyber crime matters Cross-examination almost always ventures into dangerous territory. The reason for this is that the ...
-
Indian Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) on 9th February has arrested the country's first 'darknet' narcotics operative who alleg...
-
Police Closure Reports after investigation in cyber crime cases : 1. Art 21 of the Constitution guarantees fundamental right to life and per...